This guide provides an overview of the opportunities and challenges facing cloud computing career professionals in 2024, as they strive to navigate the digital transformation.

Cloud computing has become a game-changing force in the fast-paced digital world, revolutionizing data storage, processing, and access. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud operations, pursuing a career in this field has become highly appealing. This guide offers a comprehensive roadmap, covering the fundamentals and guiding you towards a successful path in cloud computing.
1. Comprehensive Guide to Careers in Cloud Computing
a. What is Cloud Computing?
At the fundamental level, cloud computing pertains to the provision of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and other related services, through the internet. Rather than possessing and administering physical infrastructure, users can obtain access to these resources on a pay-per-use basis, commonly known as “cloud services” like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or IBM Cloud. This paradigm has supplanted the conventional method of procuring and upholding on-site hardware and software.
b. Why Cloud Computing Matters?
Cloud computing has gained popularity due to its many benefits, such as cost-effectiveness, scalability, flexibility, and ease of access. It empowers companies to streamline their processes, accelerate innovation, and effortlessly connect with audiences worldwide. Ultimately, cloud computing plays a crucial role in driving digital transformation and ensuring businesses can stay competitive in the fast-paced modern market.
c. The Growing Demand for Cloud Professionals
There are many reasons why a career in cloud computing is a good choice. First, cloud computing is a rapidly growing field. With the migration of businesses to the cloud, there has been a significant increase in the demand for cloud professionals with skills and expertise.
Companies are actively searching for individuals who can effectively design, deploy, manage, and ensure the security of cloud-based solutions. This demand is observed across diverse industries such as finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and entertainment. Consequently, pursuing a career in cloud computing not only guarantees job stability but also opens up thrilling prospects for personal growth and innovation.
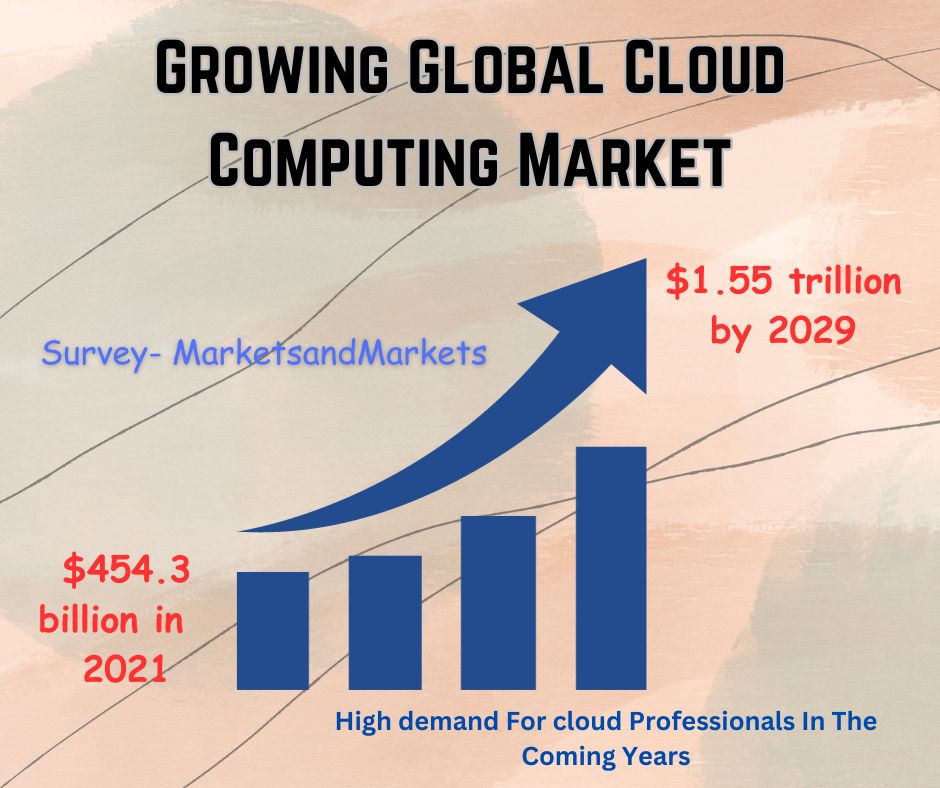
Second, cloud computing careers are well-paying. According to Indeed, the average salary for a cloud engineer in the United States is $124,357 per year. Cloud architects and cloud security engineers can earn even more.
Third, cloud computing careers offer a lot of flexibility. Many cloud professionals work remotely, and there are many opportunities to advance your career.
2. Key Cloud Computing Concepts
Before starting a career in cloud computing, it is essential to have a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts that form the basis of this technology.
a. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that offers virtualized computing resources through the internet. This service enables users to rent virtual machines, storage, and networking components, thereby facilitating the creation of virtual data centers. Prominent IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
b. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) represents an advanced approach that encompasses not only infrastructure but also development tools within its framework. This integration significantly streamlines the intricate procedures involved in application development, deployment, and management. Prominent examples of such platforms include Heroku and Google App Engine.
c. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software delivery model that provides applications to users over the internet on a subscription basis. This model enables users to access the applications through a web browser, thereby eliminating the need for local installations. Notable examples of SaaS include Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Microsoft 365.
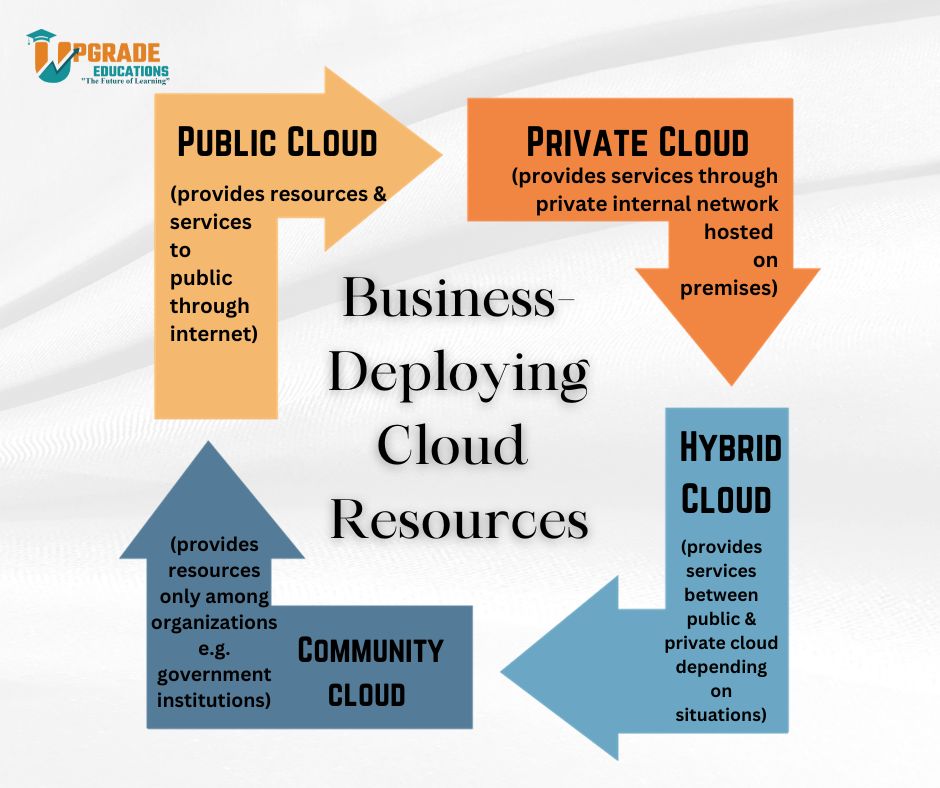
d. Primary Cloud Types: Public, Private, and Hybrid Clouds
Public clouds are managed by external service providers and are available to all users. In contrast, private clouds are exclusively reserved for a single organization and provide enhanced oversight and confidentiality. Hybrid clouds integrate public and private cloud infrastructures, facilitating the seamless transfer of data and applications between them.
3. Cloud Computing Career Paths

A career in cloud computing encompasses a range of paths, each tailored to specific skill sets and interests.
a. Cloud Architect
Cloud architects are responsible for designing cloud-based solutions that meet the technical and business requirements of an organization. They create a blueprint for the cloud infrastructure, ensuring that it aligns with security, scalability, and performance needs.
b. Cloud Developer
These professionals focus on creating and optimizing applications for cloud environments. They utilize Platform as a Service (PaaS) offerings to build, deploy, and maintain software that takes full advantage of the benefits offered by the cloud.
c. Cloud Administrators
on the other hand, are tasked with managing and monitoring cloud infrastructure. They are responsible for provisioning resources, optimizing costs, and ensuring the reliability and performance of cloud services.
d. Cloud Security Specialist:
With the increasing adoption of cloud technology, the demand for Cloud Security Specialists has also grown. These experts design and implement security measures to safeguard data and applications in the cloud.
e. Cloud Data Engineer:
Cloud Data Engineers specialize in data storage, processing, and analysis in the cloud. They utilize various big data tools and technologies to extract valuable insights from vast datasets.
f. Cloud DevOps Engineer:
DevOps Engineers play a crucial role in the cloud computing field by bridging the gap between development and operations. They ensure a smooth pipeline for deploying applications to the cloud by automating processes and managing infrastructure as code.
g. Cloud Sales and Marketing:
Lastly, professionals in Cloud Sales and Marketing roles are responsible for promoting cloud solutions to clients and customers. They play a vital role in driving adoption and revenue for cloud providers.
h. Cloud Support Engineer:
Cloud support engineers are professionals in the field of engineering who are dedicated to the maintenance and management of the backend operations and infrastructure of cloud computing. Their primary objective is to ensure the seamless and efficient functioning of cloud services. Additionally, they bear the responsibility of identifying and resolving a wide range of issues that may arise within user accounts, ranging from rudimentary to intricate problems encountered while utilizing cloud services. These engineers possess a comprehensive understanding and expertise in all domains and facets pertaining to the products offered by the company.
Tips: 💡 Grow Skills with Cloud Training
4. Skills and Qualifications For Cloud Computing Career
Acquiring a diverse set of technical skills, soft skills, and qualifications is essential for achieving success in a cloud computing career.
a. Technical Skills:
i. Cloud Platform Proficiency
In terms of technical skills, it is crucial to develop proficiency in one or more cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, or GCP. This entails gaining a deep understanding of the functionalities and features offered by these platforms.
ii. Programming and Scripting
Additionally, proficiency in programming and scripting languages like Python, JavaScript, or Ruby is necessary. Familiarity with infrastructure-as-code tools like Terraform is also important, as they enable the automation and management of cloud infrastructure.
iii. Containerization:
Furthermore, it is essential to familiarize oneself with container technologies such as Docker and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes. These technologies facilitate the efficient deployment and management of applications in a cloud environment.
iv. Networking:
Understanding cloud networking concepts is another crucial aspect of cloud computing. This includes knowledge of virtual private clouds, subnets, and load balancing, which are fundamental components of cloud networking.
v. Security:
Expertise in cloud security practices is also vital. This involves gaining knowledge of identity and access management, encryption, and compliance measures to ensure the security and integrity of cloud-based systems.
vi. Database Management:
Lastly, it is important to learn about cloud-based database services and data warehousing solutions. This includes understanding the functionalities and capabilities of these services, as well as their integration with other cloud technologies.
By acquiring these technical skills, individuals can enhance their prospects in a cloud computing career and effectively contribute to the field.
b. Soft Skills
- Communication: Effective communication is an essential component for successful collaboration within teams and for conveying complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
- Problem-solving: Cloud professionals are often confronted with intricate challenges that necessitate creative problem-solving skills.
- Adaptability: Given the constantly evolving nature of the cloud landscape, adaptability is a crucial attribute for remaining relevant.
- Project management: Familiarity with project management principles can facilitate the efficient handling of cloud projects.
c. Certifications:
Obtaining certifications from cloud providers, such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator, and Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect, can validate one’s skills and enhance career prospects.
d. Education Options:
While a formal degree in computer science or a related field can be advantageous, many cloud professionals acquire skills through online courses, bootcamps, and self-study. Continuous learning is imperative in this ever-changing field.
e. Job Market and Salary Expectations
Job Market Trends: The demand for cloud professionals in the job market remains strong and is projected to keep growing. Job postings for cloud-related positions have consistently increased year after year, indicating a continued upward trend as more organizations adopt cloud technologies.
Salary Expectations: Salary prospects in the cloud computing industry can vary significantly based on factors such as location, experience, and specialization. On average, cloud professionals receive competitive salaries. Cloud architects and engineers with several years of experience have the potential to earn six-figure salaries in numerous regions.
5. How to start a career in cloud computing
If you have an interest in pursuing a career in cloud computing, there are a few steps you can take to get started:
- Educate yourself on cloud computing/building a foundation: Take advantage of the numerous online resources and library materials that can teach you about cloud computing concepts and architecture. Additionally, consider enrolling in online courses or attending bootcamps dedicated to cloud computing to further expand your knowledge.
- Specialize in a cloud platform: With various cloud platforms available, such as AWS, Azure, and GCP, it’s important to choose one to specialize in. Once you have made your selection, delve into learning about the specific services and features offered by that particular platform.
- Gain hands-on experience: The best way to truly understand cloud computing is by putting your knowledge into practice. Set up your own cloud account and experiment with different services to gain hands-on experience. Additionally, consider participating in hackathons and other events related to cloud computing to further enhance your skills.
- Obtain certifications: Cloud computing certifications can significantly strengthen your credentials and demonstrate your expertise to potential employers. Look into various certifications available, such as the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner or the Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect Expert, and pursue the ones that align with your career goals.
- Network with fellow cloud professionals: Networking is a valuable tool for discovering job opportunities and receiving guidance from experienced cloud professionals. Utilize online platforms or attend industry events to connect with others in the field and expand your professional network.
- Creating a Portfolio: Create a comprehensive collection that highlights your cloud projects and achievements. This can be immensely valuable in both job applications and freelance pursuits.
6. Career Advancement and Specialization
Continuous Learning: The field of cloud computing is constantly changing. Keep yourself informed by keeping up with industry news, participating in webinars, and pursuing advanced certifications.
Paths to Specialization: Think about specializing in a particular area, like cloud security, machine learning in the cloud, or cloud-native development. Specializing can make you a highly sought-after expert in your chosen field.
Roles in Leadership and Management: As you accumulate experience, you have the opportunity to move into leadership or management positions. In these roles, you will be responsible for overseeing larger projects and teams.
7. Challenges and Future Trends
Cloud Computing Challenges: Although cloud computing presents a plethora of advantages, it also presents certain challenges that must be addressed. These challenges include apprehensions regarding data privacy, the possibility of vendor lock-in, and the necessity for robust security measures. It is imperative for cloud professionals to remain vigilant in addressing these issues.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing: The future of cloud computing is being shaped by several exciting trends, such as serverless computing, edge computing, and multi-cloud strategies. Familiarizing oneself with these trends and their implications can provide a competitive advantage in one’s career.
Wrapped it Up:
If you want to make it big in the cloud computing industry, you’ve come to the right place. It’s an industry that’s constantly evolving and growing, and cloud computing is no exception. Whether you want to be a cloud architect or developer, an administrator, or a specialist, you’ll need to have a solid understanding of cloud technology, stay up-to-date with the latest trends, and be flexible. Cloud computing is here to stay, and it’s going to shape the way businesses work and connect with the world for years to come. So, jump on the cloud, get your skills up to speed, and take your career to the next level.
Before you go! Leave a comment 💬 to let us know what you think about this topic. Share 📢 this article with your network to help spread knowledge.